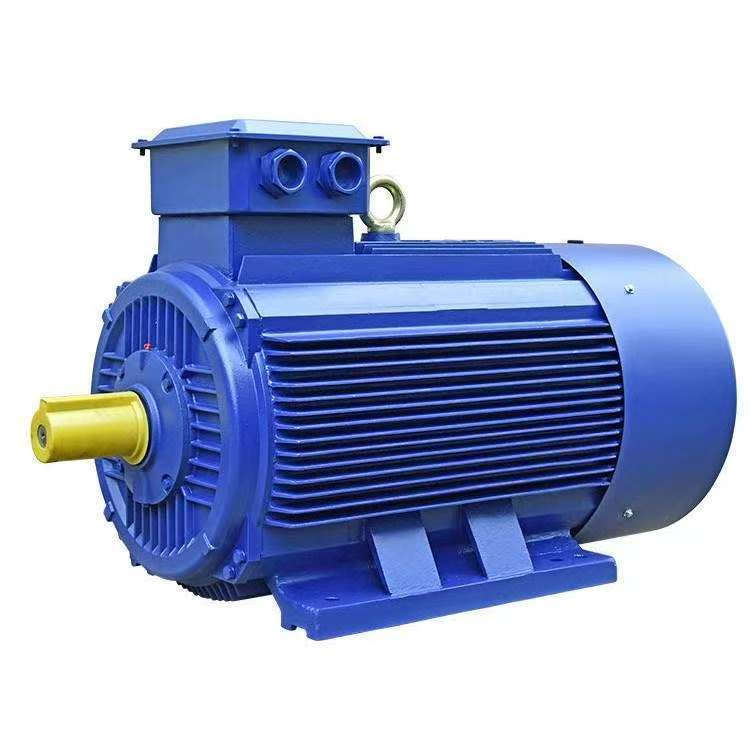
The windings of the AC three-phase asynchronous motors of Qingdao Longchangjie are mainly divided into the following types:
Classified by the arrangement form of the coils in the slot
· Single-layer winding:
Single-layer winding is a type of winding in which only one effective side of the coil is embedded in each stator slot, thus the total number of coils in it is only half of the total number of slots in the motor. The advantage of single-layer winding is that it has fewer winding coils and a relatively simple process. There is no improvement in the utilization rate of the interlayer absolute reason slot. Single-layer structures will not experience interphase breakdown faults, etc. The drawback is that the electromagnetic wave shape generated by the winding is not ideal enough. The iron loss and noise of the motor are relatively large, and the starting performance is also slightly poor. Therefore, single-layer windings are generally only used in small-capacity asynchronous motors. Single-layer windings can be classified into several types based on the shape of their coils and the arrangement of their terminal parts, such as chain windings, cross-chain windings, concentric windings, and cross-concentric windings.
1. Chain winding
Chain windings are composed of single-layer coil elements with the same shape and width. They are named so because each coil at the end of the winding resembles a chain link. It should be particularly noted that for single-layer chain windings, the pitch of the coil must be odd; otherwise, the winding cannot be arranged.
2. Cross-chain winding
When the number of slots per pole and each phase of the cross-chain winding is an odd number greater than 2, the cross-chain winding cannot be arranged. At this time, a cross-chain winding with single or double coils needs to be used.
3. Concentric winding
In concentric windings, all coils within the same pole phase group enclose the same center.
4. Cross-type concentric winding
When the number of slots Q in each phase of each stage is an even number greater than 2, the concentric winding form can be adopted.
The advantages of single-layer concentric windings and cross-concentric windings are that the winding and embedding of the windings are relatively simple, while the disadvantage is that the ends of the coils are too long and consume too much wire. Nowadays, except for the occasional use in small-capacity 2-pole and 4-pole motors, this winding form is rarely adopted nowadays.
Double-layer winding: Two coil element sides are embedded in each slot, and the number of coils is equal to the number of slots. The advantages are that the favorable pitch can be selected to improve the electromagnetic wave shape, the fractional slot winding group can be adopted to weaken harmonics, the electromagnetic performance is good, the force and energy index and starting characteristics are superior to those of the single-layer winding, the deformation at the coil end is small, which is conducive to heat dissipation and enhancing mechanical strength. The disadvantages are that the wiring is labor-intensive, there is a possibility of short circuit, insulation is required between layers, and the slot filling rate is low. It is suitable for large-capacity motors. Medium and large-sized motors generally adopt double-layer windings. Including:
. Double-layer stacked winding: Widely used in the stator and rotor windings of three-phase asynchronous motors.
. Double-layer wave winding: It is mostly used in the electronic 0 winding and wound rotor winding of hydroelectric generators.
. Single and double-layer hybrid winding: Essentially, it is a variation of the short-distance double-layer winding. Some of the upper and lower layers of the coil are combined into single-layer sides, while some remain double-layer sides, and the ends are reconnected. It can enhance motor efficiency, lower temperature, improve starting characteristics, and save copper usage, etc.
Classified by the terminal wiring method
· Stacked winding: Adjacent coils are stacked in sequence, with neatly arranged ends and a solid structure. It is widely used in the stator and rotor windings of three-phase asynchronous motors.
Wave winding: The coil connection is in a wavy shape, and it is mostly used for wound rotor windings and stator windings of large motors. The manufacturing process is relatively complex.